Imagine stumbling across something world-changing, only to let it sit on a shelf for 50 years. Sounds wild, right? That’s exactly what happened with a set of fossils found in Mongolia’s Gobi Desert in the early 1970s. For decades, these bones were boxed away, unnoticed. Now, they’ve been re-examined—and the results are shaking up dinosaur history.
Discovery
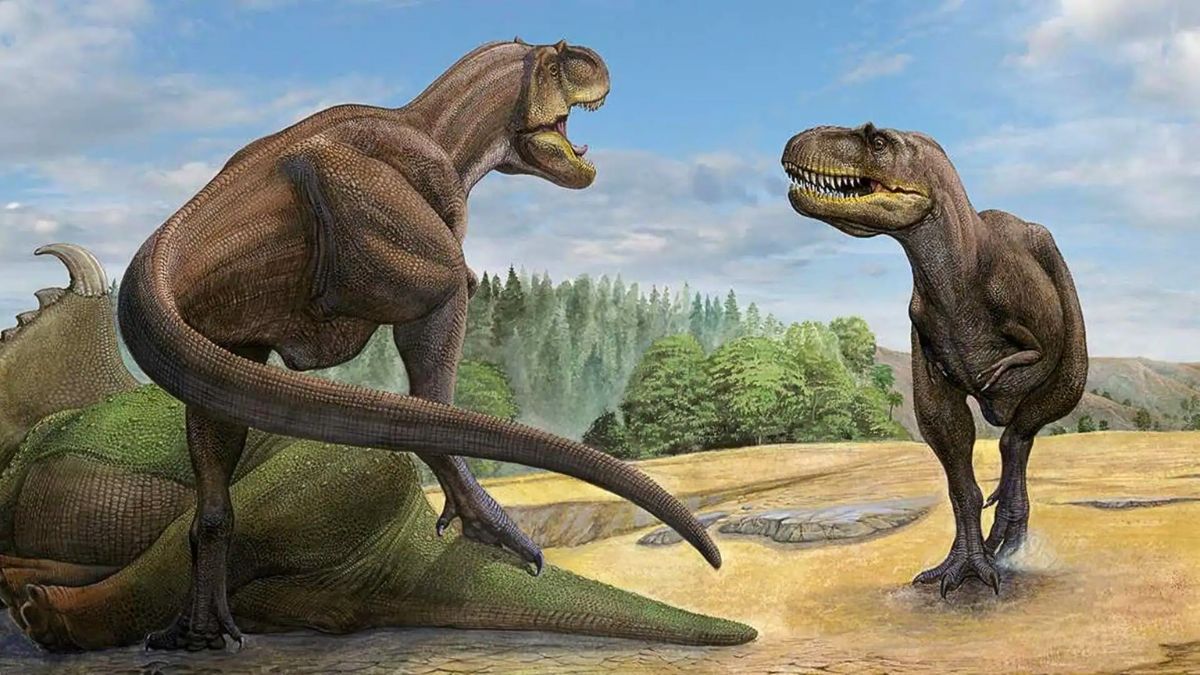
Back in 1972 and 1973, a few fossils were dug up from the Gobi Desert. Nothing flashy at the time. Scientists believed they were just more of the same: already-known species or incomplete specimens. But thanks to modern technology and a fresh look, researchers recently discovered that these fossils belong to a new species of dinosaur. Say hello to Khankhuuluu mongoliensis.
Hard to pronounce? Sure. But undeniably cool.
Relative
So what’s the big deal with this new dino? Well, Khankhuuluu mongoliensis isn’t just any dinosaur—it’s the closest known relative to the mighty T-Rex. Think of it like finding out your family tree includes a long-lost cousin who helped shape your entire bloodline. This changes the whole narrative about how T-Rexes evolved and where they came from.
While the T-Rex was a six-ton beast, the Khankhuuluu was more modest—just about 4 meters long and weighing around 750 kilos. Still, it was no pushover.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | T-Rex | Khankhuuluu mongoliensis |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 12 meters | 4 meters |
| Weight | 6 tons | 750 kilograms |
| Location | North America | Asia (Mongolia) |
| Age | 68–66 million years | ~85 million years ago |
Evolution
This discovery flips the script on the T-Rex’s family history. For years, scientists believed tyrannosaurs were a North American story. But Khankhuuluu’s bones tell a different tale. Turns out, the roots of these apex predators trace back to Asia.
Experts now believe that early tyrannosaurs crossed a land bridge between Siberia and Alaska during the Late Cretaceous period. This migration opened up a world of evolutionary possibilities, eventually leading to giants like the T-Rex.
Technology
So why did it take five decades to recognize this dino for what it really is? Simple: the tools back then just weren’t good enough. Only with today’s scanning, modeling, and analysis technologies could paleontologists fully understand what they were looking at.
Sometimes, the answers are right under our noses—but we need the right lens to see them.
Impact
The implications of this discovery go beyond just naming a new species. It’s pushing scientists to revisit old fossils, reevaluate theories, and dig deeper—literally and figuratively. Paleontology is like detective work, and Khankhuuluu just opened up a cold case that could lead to even more surprises.
This new dino is more than a scientific curiosity. It’s a reminder that history is still being written, and sometimes, it just takes a second look to uncover something incredible.
And who knows? Those dusty old bones in the back of the museum might just hold the next game-changer.
FAQs
What is Khankhuuluu mongoliensis?
A newly identified dinosaur species closely related to T-Rex.
Where was it discovered?
In the Gobi Desert, Mongolia, in the early 1970s.
How big was Khankhuuluu?
About 4 meters long and weighed 750 kilos.
Why is this discovery important?
It reshapes the evolutionary tree of tyrannosaurs.
What does it mean for T-Rex origins?
It confirms tyrannosaurs originated in Asia.